Introduction to AI Humanoid Robots
AI humanoid robots represent a significant advancement in robotics, characterized by their human-like appearances and behaviors. Unlike traditional robots that are generally designed for specific tasks with little consideration for human interaction, AI humanoid robots possess the ability to mimic human actions and emotions, making them more adept at engaging with people. This unique capability stems from the integration of artificial intelligence, which empowers these robots to understand and respond to human communication and behaviors, thus enhancing their functionality and the overall user experience.
The evolution of humanoid robots has transitioned from basic mechanical designs to sophisticated AI-driven systems. Initially, humanoid robots were primarily constructed to showcase engineering prowess and perform straightforward functions. As technology progressed, the focus shifted towards creating robots that not only look like humans but can also interact with their environment in a nuanced manner. This transformation has been fueled by advancements in machine learning, natural language processing, and sensor technologies, enabling these robots to perform complex tasks and engage in meaningful interactions with humans.
The significance of AI technology in the development of humanoid robots cannot be overstated. It has opened new pathways for these machines in various sectors, including healthcare, hospitality, and entertainment. For example, in healthcare, humanoid robots are being utilized as companions for the elderly, providing emotional support and helping to alleviate feelings of loneliness. In hospitality, AI humanoid robots serve as receptionists or concierge aides, enhancing customer experience through personalized interaction. As interest in these applications continues to grow, the potential for AI humanoid robots to transform human life becomes increasingly evident, positioning them as pivotal players in the future of robotics.
Sophia
Sophia, developed by Hanson Robotics, stands out as one of the most iconic AI humanoid robots. Launched in 2016, this robot gained worldwide recognition for her ability to engage in natural conversations, simulate human expressions, and her sophisticated AI capabilities. Sophia has been designed to learn from interactions with people, making her an effective tool for educational purposes, customer service, and public relations. Moreover, her lifelike appearance complements her functionality, allowing her to engage with human emotions effectively.
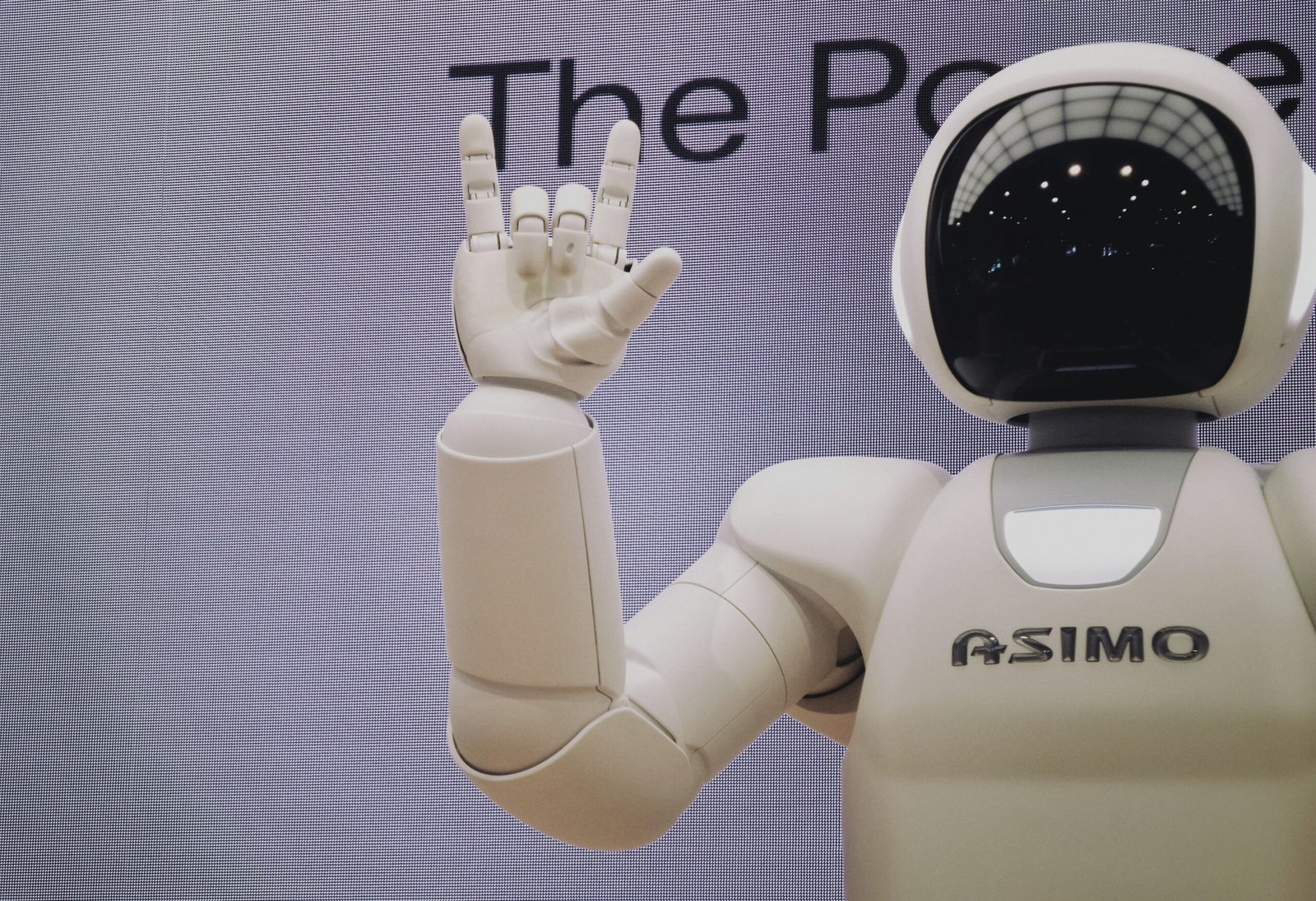
ASIMO
ASIMO, created by Honda, is renowned for its advanced locomotion capabilities. Introduced in 2000, ASIMO can walk, run, climb stairs, and navigate complex environments, making it a valuable asset for various industries, including healthcare and logistics. Its ability to interact with humans through voice commands and recognize gestures enhances its role as a personal assistant and a companion robot. The technology embedded in ASIMO represents a significant milestone in robotics, showcasing the potential of AI in creating robots that can operate alongside humans.
Atlas
Atlas, designed by Boston Dynamics, is a bipedal robot that exemplifies remarkable agility and mobility. Originally devised for search and rescue missions, Atlas can traverse through uneven terrains while performing dynamic tasks such as jumping, flipping, and lifting objects. The AI technology used in Atlas allows it to adapt to real-time obstacles, thereby broadening its utility in emergency situations and disaster recovery efforts. Its robust design and functionality present a paradigm shift in how robots can assist humans in challenging environments.
Pepper
Pepper, an emotional humanoid robot from SoftBank Robotics, focuses on human interaction and companionship. Launched in 2014, Pepper is equipped with a tablet interface and can read human emotions, responding accordingly to create a more engaging experience. This robot is primarily used in retail environments, hospitals, and educational institutions, where it helps improve customer service and enhance user engagement. By integrating AI with user-friendly interactions, Pepper plays a critical role in human-robot collaboration and companionship.
Geminoid
Geminoid, created by Hiroshi Ishiguro, is known for its strikingly realistic human-like appearance. Mimicking its human counterpart, Geminoid can reproduce a range of facial expressions and respond to conversations with high fidelity. The robot’s application primarily lies in research and social interaction, delving into the psychological effects of human-robot relationships. The unique design and functionality demonstrate how AI humanoid robots can bridge the gap between humans and artificial intelligence.
NAO
NAO, another innovation from SoftBank Robotics, is a small humanoid robot designed for educational purposes. Standing just 58 centimeters tall, NAO can walk, talk, and recognize faces, providing a platform for teaching coding and robotics. Its capabilities make it an excellent tool in classrooms, promoting STEM education among students. NAO serves as a bridge to introduce young learners to the world of AI and robotics, sparking interest and curiosity in future technological advancements.
Digital Emily
Digital Emily, developed by Image Metrics, focuses on the entertainment industry, particularly in creating lifelike virtual characters. This humanoid robot employs advanced facial recognition and rendering technologies, enabling it to mimic human expressions accurately. The integration of AI technology allows for real-time interactions in video games and movies, pushing the boundaries of virtual reality. Digital Emily symbolizes the potential of AI to transform entertainment and media experiences through human-like characters.
RoboCop
RoboCop, a fictional character that exemplifies the integration of robotics and law enforcement, highlights the potential applications of AI humanoid robots in public safety. While not a functional robot in reality, the concept behind RoboCop embodies the aspirations of utilizing AI technology in policing. As real-world technologies evolve, the possibility of using humanoid robots for surveillance and security measures becomes increasingly feasible, showcasing the impact AI can have on safety and societal protection.
Bandit
Bandit, developed for research at the University of Pennsylvania, is designed to enhance human-robot interaction in everyday tasks. Equipped with algorithms for social engagement and machine learning, Bandit can engage hobbies such as playing games and performing simple tasks in a home environment. As a service robot, Bandit represents a growing trend in robotics that emphasizes ease of interaction and companionship in domestic settings, showcasing how AI can improve daily living standards.
Erica
Erica, a humanoid robot designed by Hiroshi Ishiguro, combines cutting-edge AI with conversational abilities. Known for her engaging personality, Erica can participate in dialogues, express emotions, and adapt her interactions based on the user’s responses. This robot primarily serves in settings like interviews and presentation scenarios, contributing to discussions about the ethical implications of AI and humanoid robots in society. Erica’s development marks a significant step forward in understanding interaction paradigms between humans and robots.
Effects of AI Humanoid Robots on Human Life
The advent of AI humanoid robots has marked a significant turning point in various aspects of human life. These sophisticated machines are increasingly integrated into industries, healthcare, education, and even personal assistance. A key benefit is the enhanced efficiency that AI humanoid robots bring to different sectors. For example, in manufacturing, robots can perform repetitive tasks with precision and speed, resulting in increased productivity and reduced operational costs. This advancement enables human workers to focus on more complex and creative aspects of their jobs.
In the realm of caregiving and healthcare, AI humanoid robots have emerged as invaluable tools. They assist with routine tasks such as medication reminders, mobility support, and even companionship for the elderly. These robots can provide a level of monitoring and assistance that allows caregivers to focus on more personalized care, significantly improving the quality of life for patients. In education, robots are revolutionizing teaching methodologies. They can tailor lessons to individual student needs, provide real-time feedback, and engage learners in interactive ways, making education more accessible and effective.
However, the integration of AI humanoid robots is not without its drawbacks. One of the most pressing concerns is job displacement. As robots take over tasks traditionally performed by human workers, there is a fear of redundancy, particularly in low-skilled job markets. Additionally, ethical issues surrounding AI usage, including privacy concerns and the potential for biased programming, raise questions about accountability and responsibility. Furthermore, the necessity for social acceptance is paramount, as the public’s perception of humanoid robots can impact their adoption.
Real-world instances, like the use of robot-assisted surgeries, demonstrate the benefits of AI humanoid robots while showcasing the ethical and societal challenges that must be addressed. Balancing these effects is critical to ensuring that the advancement of AI technology positively contributes to society.
The Future of AI Humanoid Robots
The evolving landscape of AI humanoid robots suggests a future rife with advancements that promise to significantly influence various aspects of human life. As technology continues to progress, we can anticipate enhanced capabilities in these robots, fundamentally altering their roles in society. Current research in robotics and artificial intelligence highlights several trends that will likely shape the future of humanoid machines. For instance, improvements in machine learning algorithms will enable robots to better understand and navigate complex environments, allowing them to interact more effectively with humans.
Furthermore, advancements in sensors and actuators are expected to refine the physical abilities of humanoid robots, resulting in more natural movements and interactions. This will expand their applicability across diverse domains, from healthcare, where they could assist patients or even conduct surgeries, to education, helping teach and engage students in innovative ways. As the potential applications grow, so too will discussions surrounding the ethical implications of deploying humanoid robots in everyday life. These ethical considerations will require careful attention to ensure that developments align with societal values and norms.
The impact of humanoid robots is not solely limited to functionality; it also encompasses broader societal changes. As robots become more integrated into our daily lives, there will likely be shifts in workforce dynamics, necessitating policy adjustments to address challenges such as job displacement or the redistribution of labor. While some tasks may be automated, new opportunities may emerge in fields related to the development, maintenance, and ethical oversight of these advanced machines. This evolution will require collaboration among technologists, policymakers, and ethicists to establish guidelines that both promote innovation and safeguard human well-being.
In the coming years, the intersection of AI, robotics, and human interaction will undoubtedly usher in significant changes, ultimately redefining our relationship with technology and highlighting the need for a proactive approach to its advancement.